In the inland waterway transportation system, navigation buoys play an important role in guiding and ensuring safety for vessels. To standardize management and improve operational efficiency, Vietnam has issued national technical regulations that clearly define standards for the design, manufacturing, installation, and inspection of navigation buoys. NLT Group will systemize all relevant content related to the currently applied regulations, helping organizations and individuals understand and implement them correctly in practice.
Overview of inland waterway navigation buoys
The importance of navigation buoys in inland waterway transport
Navigation buoys are essential elements that ensure safety and regulate navigation channels for moving vessels. They help provide direction, warnings, and necessary information for operators, especially in bad weather conditions or at night.
Using the correct type of inland buoy according to regulations not only helps vessels avoid hazardous areas but also supports effective management and maintenance of the waterway transport system.
Why are national technical regulations for navigation buoys necessary?
Issuing national technical regulations aims to standardize the design, manufacturing, and use of inland waterway navigation buoys nationwide. This not only enhances management efficiency but also ensures safety for waterway transportation activities, aligning with international standards and practical conditions in Vietnam. The issuance of National Technical Regulations (QCVN) is a mandatory step to:
- Standardize design, color, shape, and technical specifications of buoys nationwide.
- Provide a legal basis for organizations involved in manufacturing, construction, inspection, and supervision of navigation buoys.
- Ensure compatibility and integration with international maritime marking systems, such as IALA standards.
- Support digitalization and automation in waterway traffic monitoring, as more buoys integrate IoT technology, AIS, or solar-powered lighting.
Legal framework for buoy standards in vietnam

QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT – Inland waterway signaling
This is the National Technical Regulation on the inland waterway signaling system of Vietnam, issued under Circular No. 08/2020/TT-BGTVT dated April 17, 2020, replacing QCVN 39:2011/BGTVT.
Some main contents:
- Scope of application: Applies to all organizations and individuals involved in the design, construction, management, operation, and maintenance of inland waterway signaling within the territory of Vietnam.
- Classification of signals: Includes buoys, signboards, beacons, lights, and others based on function (channel marking, hazard warning, special area signaling).
- Technical requirements:
- Standardized colors, shapes, and dimensions (for example: port side buoy red, starboard side buoy green).
- Regulations on minimum visibility range for buoy lights at night.
- Rules for marking symbols and identification numbers on buoy bodies for unified management.
QCVN 72:2022/BGTVT – Classification and manufacturing of mooring buoys and signal buoys
This is the national technical regulation on classification and manufacturing of signal buoys, especially sea mooring buoys and maritime navigation buoys, issued by the Ministry of Transport in 2022 to replace and update previous technical standards.
Some key points:
- Classification of buoys based on load class, size, and operating zones (coastal, river mouth, offshore).
- Material requirements: buoys must be made from corrosion resistant materials capable of withstanding saltwater environments.
- Manufacturing and inspection requirements: each buoy must have complete technical documentation, design drawings, buoyancy test reports, and structural strength reports before delivery.
This regulation helps ensure that contractors, manufacturers, vessel owners, and authorities comply with standards throughout the buoy lifecycle.
Related circulars (08/2020/TT-BGTVT, 45/2021/TT-BGTVT…)
Circular 08/2020/TT-BGTVT: Issued together with QCVN 39:2020, providing the legal basis for applying the inland waterway signaling system.
Circular 45/2021/TT-BGTVT: Although it does not directly regulate buoy standards, it includes provisions related to toll station organization and inland waterway traffic management.
Classification of buoys by function
Channel marking buoys

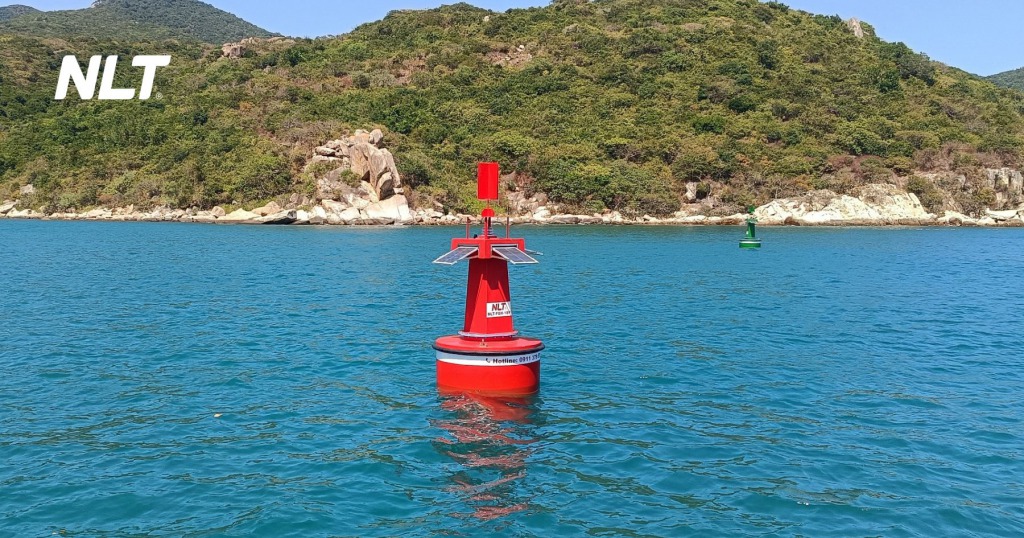
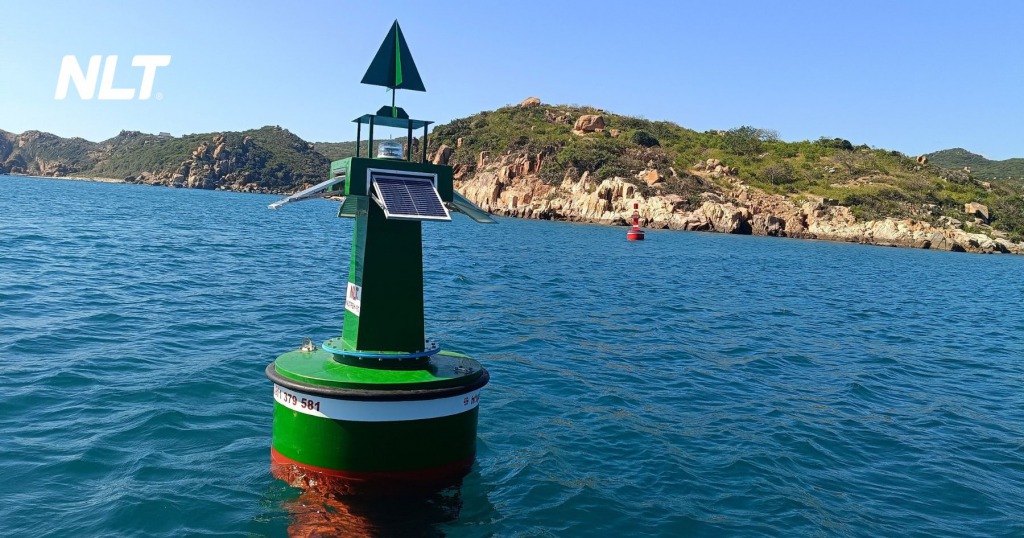
Channel marking buoys are used to define the boundaries of navigation channels, helping vessels orient and travel safely. According to QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT, channel buoys include:
- Port side buoys: painted red, conical shape, red light.
- Starboard side buoys: painted green, cylindrical shape, green light.
- Mid channel buoys: painted red and white stripes, spherical shape, white light.
These buoys are placed along navigation routes to help operators identify and follow the correct direction, especially important in bad weather or at night.
>> See more: Inland waterway navigation signage system under national technical regulations
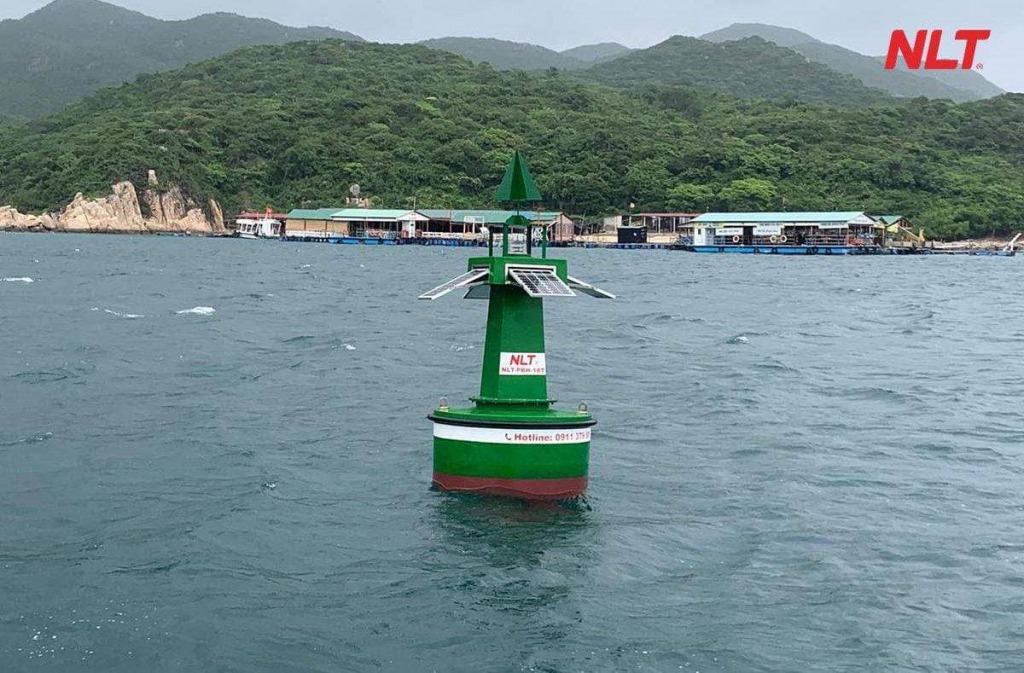
Hazard marking buoys
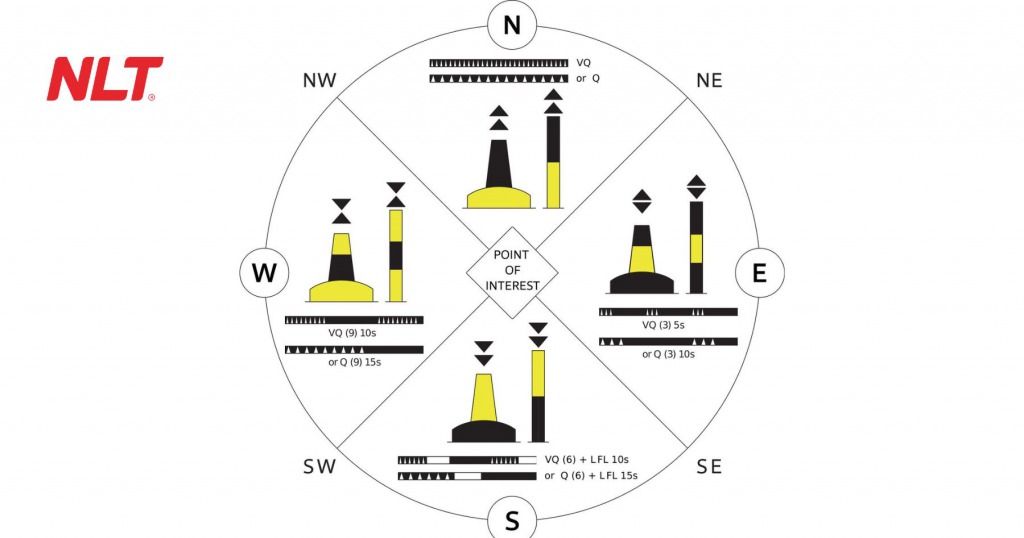
Hazard marking buoys are used to warn about obstacles or dangerous areas along navigation routes, such as submerged rocks, underwater structures, or other hazards. According to QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT, these buoys have the following characteristics:
- Color: yellow.
- Shape: cylindrical or conical.
- Light signal: yellow, flashing twice every 10 second cycle.
Recognizing and complying with hazard buoys helps vessels avoid dangerous zones and ensures safe navigation.
Special area and restricted zone buoys
Special area or restricted zone buoys are used to indicate areas with specific regulations such as no anchoring zones, military areas, or special operation zones. According to QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT, these buoys have the following characteristics:
- Color: yellow.
- Shape: cylindrical or conical.
- Light signal: yellow, flashing five times every 20 second cycle.
These buoys help vessel operators recognize and comply with special regulations, ensuring safety and legal compliance.
Mooring buoys and maritime signal buoys

Mooring buoys and maritime signal buoys are used in sea and port areas to support vessel anchoring and provide navigation information for maritime traffic. According to QCVN 20:2015/BGTVT, these buoys include:
- Mooring buoys: used to define safe anchoring positions for vessels.
- Maritime channel buoys: used to guide and identify safe maritime routes.
- Restricted area buoys: used to indicate prohibited or limited maritime zones.
These buoys have specific technical characteristics and requirements defined in QCVN 20:2015/BGTVT to ensure safety and operational efficiency in maritime activities.
Technical requirements for buoys under QCVN

Requirements on shape, dimensions, and color
According to QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT, inland waterway navigation buoys must comply with requirements on shape, dimensions, and color to ensure clear and consistent identification.
- Shape: Must match the function of each buoy type; for example, a left-side channel buoy has a conical shape, while a right-side channel buoy has a cylindrical shape.
- Dimensions: Divided into four categories: special, Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3, with specific sizes defined in the appendix of the regulation.
- Color: Painted in characteristic colors according to function; for example, left-side buoys are painted red, right-side buoys green, and hazard-marking buoys yellow.
Requirements on manufacturing materials and durability
Navigation buoys must be manufactured from durable materials capable of withstanding water environments and harsh weather conditions.
- Materials: Priority is given to materials such as galvanized steel, composite plastic, aluminum, wood, or other corrosion-resistant materials.
- Thickness: For steel buoys, the minimum shell thickness is 5 mm to ensure durability and service life.
Requirements on illumination capability and signal lights
To ensure safety at night or in poor weather conditions, navigation buoys must be equipped with signal lights that meet the following requirements:
- Light color: Must correspond to the buoy’s function; for example, red lights for left-side buoys, green lights for right-side buoys, and yellow lights for hazard buoys.
- Visibility range: Lights must have a minimum visibility range of 1,000 m under good weather conditions.
- Flash characteristics: Specifically defined in the regulation; for example, single flash, double flash, or rapid continuous flashing depending on the buoy type.
Regulations on buoy identification numbers and markings
Each navigation buoy must be clearly labeled with identification numbers and markings to support management and navigation:
- Identification number: Assigned according to the management system to determine the buoy’s position and function.
- Markings: Must clearly indicate the buoy type, function, and other necessary information, painted or attached to the buoy body in a visible and recognizable manner.
Inspection, classification, and certification procedures for buoys
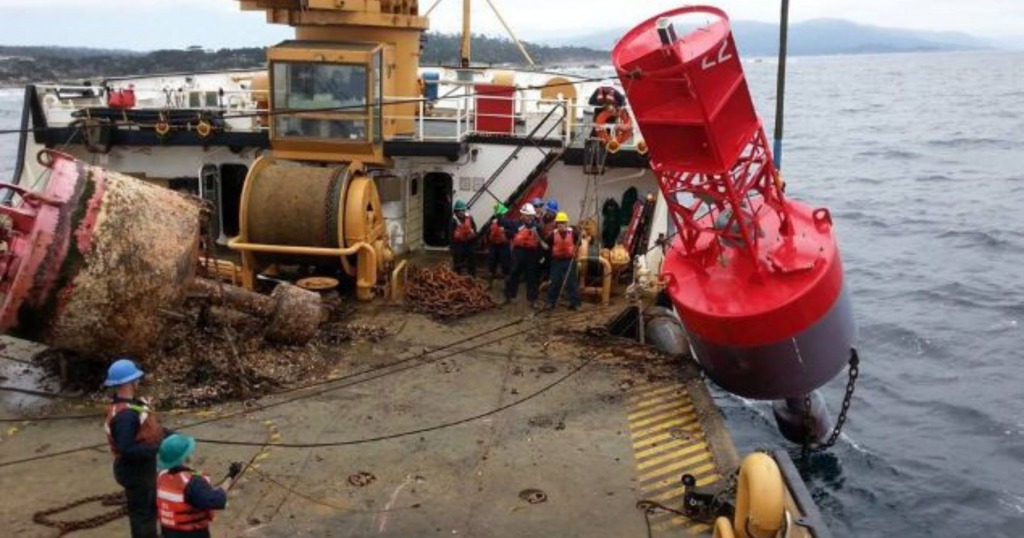

Inspection of design and manufacturing
Before being put into operation, navigation buoys must undergo design and manufacturing inspections to ensure compliance with national technical regulations. According to QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT, inspection steps include:
- Design appraisal: Reviewing drawings, technical specifications, and materials to ensure suitability with the buoy’s function and operating environment.
- Manufacturing process inspection: Supervising production to ensure compliance with the approved design.
- Product quality assessment: Checking dimensions, shape, color, and other technical characteristics after completion.
Load testing, buoyancy testing, and durability testing
After completion, buoys must be tested for load capacity, buoyancy, and durability to ensure safe operation. Testing includes:
- Load testing: Evaluating the buoy’s load-bearing capacity under different conditions.
- Buoyancy testing: Verifying flotation performance in real water environments to ensure the buoy does not sink or capsize.
- Durability testing: Assessing resistance to mechanical and environmental impacts such as collision, corrosion, UV radiation, temperature, and humidity.
>> See more: Guidelines for handling damaged buoys in compliance with inland waterway regulations
Technical safety certification and registration
After completing all inspections, the buoy will be granted a technical safety certificate and registration by the competent authority. This process includes:
- Technical documentation review: Examining documents related to design, manufacturing, and inspection.
- On-site inspection: Conducting direct checks to confirm technical specifications and product quality.
- Certification issuance: If requirements are met, the authority issues a technical safety and registration certificate, allowing the buoy to be put into operation.
The role of buoys in the inland waterway traffic management system
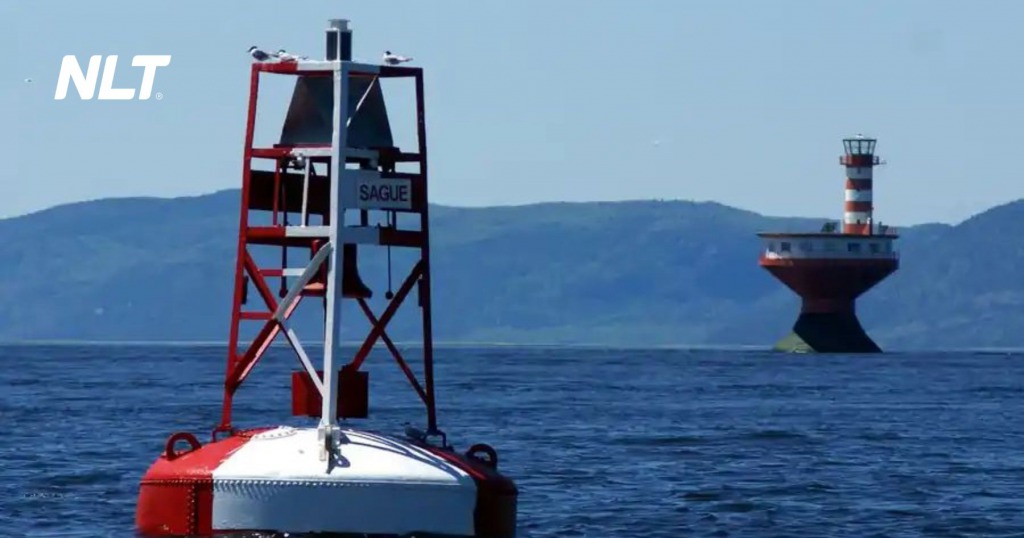

Regulating channels and guiding vessels
Navigation buoys play an important role in regulating channels and guiding vessels to move safely along inland waterways. They help to:
- Define channel boundaries: Buoys mark safe and hazardous areas, helping vessels avoid collisions and grounding.
- Provide directional guidance: Buoys indicate the correct navigation direction, especially in bad weather conditions or at night.
- Warn of hazards: Buoys alert vessels to obstacles, restricted areas, or shallow waters, helping them avoid danger.
Supporting the digitalization of inland waterway maps
Navigation buoys provide essential data for the digitalization of inland waterway maps, supporting traffic management and operations. They help to:
- Update channel information: Data from buoys is used to update channel routes, depths, and obstacles on digital maps.
- Support traffic operations: Information from buoys enables authorities to manage traffic more efficiently, reducing congestion and accidents.
- Improve management efficiency: Digital mapping helps authorities manage and maintain inland waterway systems more effectively.
Integration with IoT and remote monitoring devices
Integrating IoT technology and remote monitoring devices into navigation buoys enhances management and maintenance efficiency. Benefits include:
- Real-time monitoring: IoT devices allow remote, real-time tracking of buoy status such as position, battery level, and signal light condition.
- Rapid incident detection: Remote monitoring systems help quickly detect and address issues such as signal loss, damage, or drifting buoys.
- Reduced maintenance costs: Remote monitoring minimizes the time and cost required for inspection and maintenance.
Responsibilities of relevant stakeholders

Manufacturing and installation facilities
Facilities responsible for manufacturing and installing inland waterway navigation buoys must ensure products comply with national technical regulations. Specifically, they must:
- Comply with technical design: Manufacture buoys according to approved designs, ensuring specifications for size, shape, color, and materials.
- Conduct quality inspections: Perform necessary checks to ensure buoy quality before installation.
- Maintenance and repair: Ensure stable operation through periodic maintenance and timely repairs when necessary.
Vessel owners and port management units
Vessel owners and port management units are responsible for complying with national technical regulations on inland waterway navigation aids, including:
- Following buoy instructions: Operate vessels according to buoy guidance to ensure traffic safety.
- Incident reporting: Promptly notify authorities when buoys are damaged, lose signal, or shift position.
- Maintenance coordination: Cooperate with authorities in buoy maintenance and repair when required.
Inspection and technical supervision authorities
Inspection and technical supervision authorities play a key role in ensuring the quality and safety of inland waterway navigation buoys. Their responsibilities include:
- Inspection and quality assessment: Conduct periodic and unscheduled inspections to evaluate buoy condition and performance.
- Certification issuance: Grant technical safety certificates to buoys that meet required standards.
- Violation handling: Detect and address violations related to inland waterway navigation aids.
Important notes when selecting and using buoys in compliance with regulations
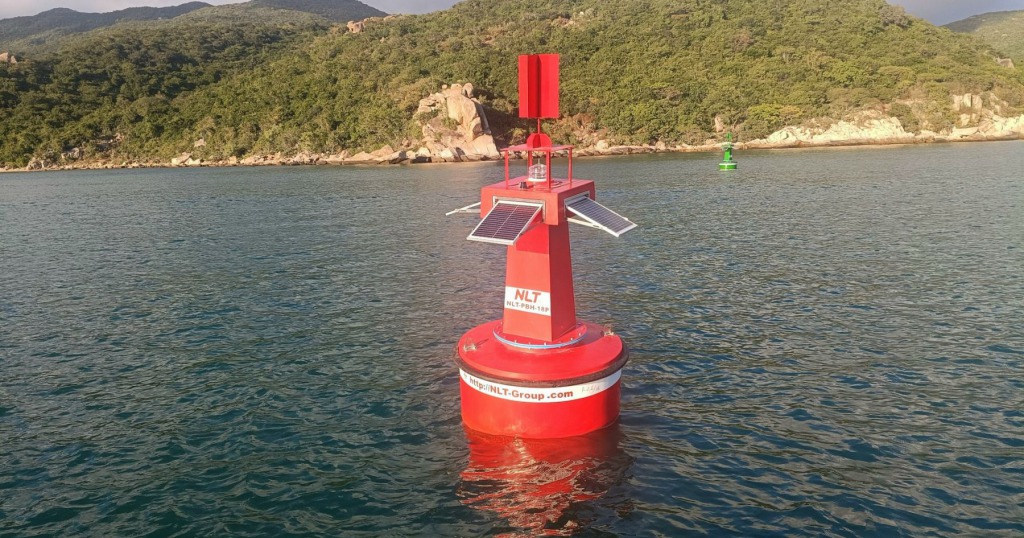

Misidentification of buoy types – consequences and solutions
Incorrect identification of buoy types may lead to serious consequences such as:
- Traffic safety risks: Vessels may enter hazardous areas or fail to follow designated channels.
- Damage to property and human safety: Inland waterway accidents may occur, causing material loss and injury.
- Legal violations: Vessel owners may face administrative or criminal penalties for violating navigation aid regulations.
Corrective measures include:
- Training and awareness: Organize training programs for vessel operators on recognizing and complying with buoy signals.
- Regular inspection and maintenance: Ensure buoys remain in good condition and positioned correctly.
Quick tips for checking compliance via labels or specifications
To quickly verify whether a buoy complies with regulations, consider the following:
- Check labels and identification numbers: Standard-compliant buoys typically have clear labels showing manufacturer information, production year, and product codes.
- Compare with regulations: Match buoy specifications with requirements in QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT.
- Observe physical condition: Check for damage, fading color, or malfunctioning signal lights.
When replacement or reporting deviations is required
Buoys should be replaced or reported in the following situations:
- Damaged or non-functional buoys: When a buoy no longer operates properly or loses its light signal.
- Displaced buoys: When a buoy is no longer positioned according to regulations, potentially causing confusion for operators.
- No longer suitable for actual conditions: When channel conditions change or waterway planning is adjusted.
In these cases, authorities should be notified promptly for handling and replacement.
>> See more: A practical guide to choosing standard-compliant inland waterway buoys for the right purpose
Conclusion
Navigation buoys are indispensable components of the inland waterway transportation system, serving to guide, warn, and ensure safety for vessels. The development and consistent application of national technical regulations such as QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT and QCVN 72:2022/BGTVT have established a clear and unified legal framework for the design, manufacturing, installation, operation, and inspection of navigation buoys nationwide. For related organizations and individuals, understanding and strictly complying with national technical regulations is a mandatory condition to ensure legality, safety, and efficiency in waterway transportation activities.
FAQ
Which national technical regulation is currently the latest applied for inland waterway buoys?
Currently, the latest standard is QCVN 39:2020/BGTVT – National Technical Regulation on Inland Waterway Signaling of Vietnam. In addition, for maritime buoys, offshore signal buoys, and mooring buoys, QCVN 72:2022/BGTVT and other specialized regulations may also apply.
How long is the technical inspection period for buoys?
Typically, technical inspection for buoys is conducted annually for buoys under specialized registration and management. However, depending on actual conditions, management authorities may require unscheduled inspections or shorter inspection cycles if signs of damage, misalignment, or harsh environmental conditions appear.
Are solar-powered lights mandatory on buoys?
They are not mandatory for all buoy types, but solar-powered lights are encouraged to ensure continuous illumination efficiency, reduce operating costs, and align with green transition trends in waterway transportation. Some key waterway routes already require buoys integrated with automatic lighting to enhance nighttime safety.
Which authority must be registered with to obtain installation approval for buoys?
The installation of navigation buoys falls under the management scope of the Vietnam Inland Waterways Administration or provincial Departments of Transport (for local routes). Investors must prepare signaling design documents, obtain technical agreement, and receive approval before installation.
Is it allowed to self-manufacture buoys for internal use?
Organizations and businesses may manufacture buoys for internal use (for example, in private ports or aquaculture areas), but they must still comply with national technical regulations, undergo inspection if required, and must not alter functionality or cause confusion with public navigation buoys.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt






