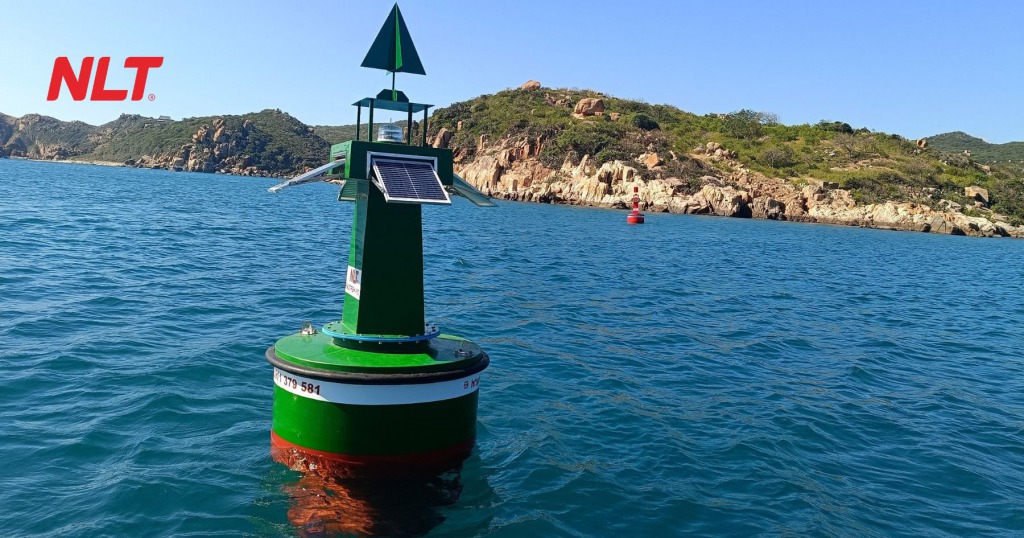
In the field of inland waterway transportation, where navigation aids such as buoys must operate continuously outdoors and withstand sun exposure, rain, saltwater, and physical impact, the choice of manufacturing material plays a decisive role in durability and operational efficiency. HDPE rotomolding (rotationally molded polyethylene plastic) is gradually becoming the industry standard for floating buoy production thanks to its outstanding technical properties, high durability, and environmental friendliness. This article by NLT Group will help you clearly understand why HDPE rotomolding is the leading choice for the new generation of modern waterway buoys.
What is HDPE rotomolding?

Introduction to HDPE rotomolding material and rotational molding technology
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is a high-density thermoplastic that is widely used in industry thanks to its toughness, high impact resistance, water impermeability, and chemical resistance. When combined with rotational molding technology, a manufacturing technique that forms hollow products by rotating the mold simultaneously on two axes while heating HDPE, the result is a product with a seamless monolithic structure, no joints, and high mechanical strength.
The difference between rotationally molded HDPE and injection-molded plastics
Unlike injection molding or blow molding, which typically produce thin-walled products or create welded seams, rotationally molded HDPE allows the formation of:
- Hollow products with large dimensions such as containers and buoy shells
- Uniform surfaces with no weld lines and no risk of leakage
- Adjustable wall thickness across different areas of the product
As a result, rotationally molded HDPE buoys can withstand water pressure, impact forces, and thermal expansion far better than conventional plastics.
Why this technology is suitable for floating equipment, especially buoys
Floating buoys are fixed installations in rivers and seas, requiring high levels of waterproofing, stable buoyancy, and impact resistance. HDPE rotomolding produces hollow buoy bodies that can be filled with polyurethane foam to enhance buoyancy and prevent sinking even if the shell is cracked. In addition, this technology allows technical grooves, mounting hooks, and locking rings to be integrated directly during the molding process, helping optimize production workflows and reduce installation costs.
Outstanding advantages of HDPE rotomolding in buoy manufacturing

Seamless monolithic structure with zero leakage risk
HDPE rotomolding products are formed as a single piece in a closed mold, with no welds or joints. This completely eliminates the risk of:
- Water ingress into the buoy interior
- Structural failure caused by vibration or impact at joint points
- Corrosion due to exposed adhesive seams
This is why many modern manufacturers are choosing HDPE rotomolding to replace welded plastics and welded metal structures.
High buoyancy, lightweight design, and easy installation
HDPE has a low density (approximately 0.95 g/cm³), making it lighter than water and significantly lighter than metal. When combined with rotational molding to create hollow or foam-filled structures:
- Buoys maintain stable buoyancy
- Overall weight is reduced, lowering transportation and installation costs
- Buoys can be relocated or replaced easily without heavy specialized equipment
UV resistance, corrosion resistance, and durability of up to 10–15 years outdoors
HDPE rotomolding offers excellent resistance to ultraviolet radiation. When used in outdoor equipment such as navigation buoys, HDPE maintains:
- Long-lasting color stability (red, green, yellow according to standards)
- Non-brittle surfaces that do not crack under sunlight, wind, or high temperatures
- Resistance to rot, oxidation, and degradation in brackish or saltwater
Many manufacturers have demonstrated that the actual service life of HDPE rotomolding buoys can reach 10–15 years without replacement.
No reaction with saltwater and no chemical absorption
Unlike steel, which rusts, or composite materials, which may experience adhesive layer degradation, HDPE is chemically inert to:
- Seawater, brackish water, and saline environments
- Oils, grease, diluted acids, and industrial alkalis
This allows HDPE buoys to operate reliably in seaports, industrial zones, and polluted rivers where other materials are prone to corrosion.
Easy maintenance and environmentally friendly recyclability
HDPE buoys require minimal maintenance beyond periodic checks of positioning and signal lights. When replacement is necessary:
- HDPE buoy shells can be crushed, remelted, and recycled into plastic pipes, pallets, or consumer products
- No toxic waste is generated, and no special waste treatment is required
This aligns well with current trends toward sustainable and environmentally friendly inland waterway transportation.
Specific applications of rotationally molded HDPE in navigation buoys
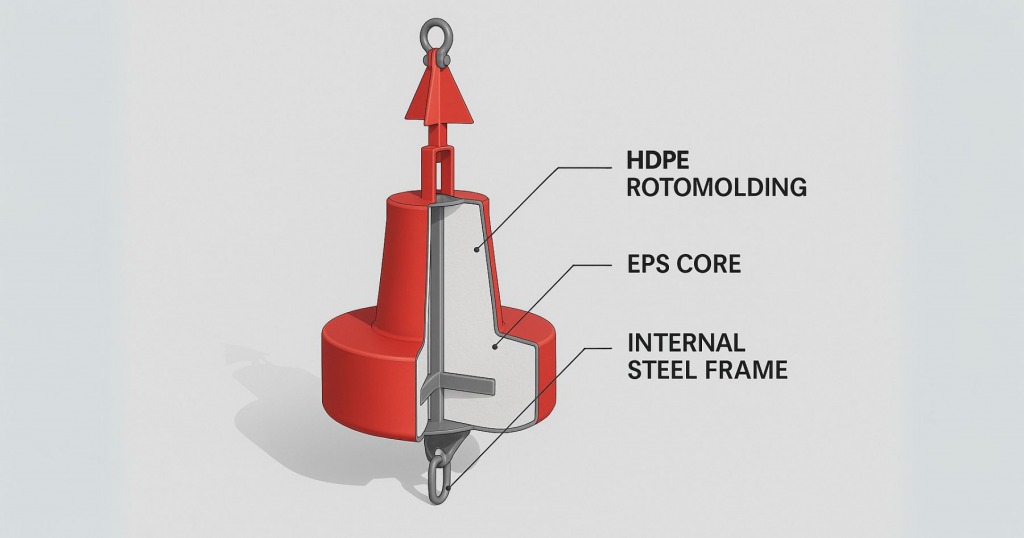
Floating buoy body – the primary load-bearing and buoyant structure
The buoy body is the most critical structure of the entire device, determining buoyancy, stability, and impact resistance. With HDPE rotomolding, the buoy body:
- Is molded as a seamless monolithic structure, ensuring complete watertightness
- Can be filled with waterproof foam inside to enhance buoyancy
- Allows easy integration of components such as mooring hooks, lifting rings, and swivel joints
Buoys using HDPE bodies are typically 40–60% lighter than steel buoys of the same size, helping reduce installation and transportation costs.
Buoys for hazardous area warnings, anchorage zones, and channel marking
HDPE rotomolding is highly suitable for manufacturing various types of buoys, including:
- Yellow buoys warning of reefs and underwater obstacles
- Red and green buoys for inland waterway channel marking
- White or black buoys marking restricted areas or anchorage zones
Thanks to direct color molding, these buoys do not require external painting, retain color for a long time, and remain highly visible from a distance even in poor weather conditions.
Protective outer shells for lighting, batteries, and GPS in smart buoys
HDPE rotomolding is non-conductive, does not block signals, and offers excellent waterproofing and impact resistance, making it ideal for:
- Housings for LED signal lights
- Casings for solar batteries and GPS units
- Protection for tilt sensors and light sensors in smart buoys
The seamless design helps protect electronic components from water ingress and thermal shock, while also allowing easy disassembly for maintenance when required.
Comparison between HDPE rotomolding and other materials
| Criteria | HDPE rotomolding | FRP (Composite) | Galvanized steel / stainless steel | Injection-molded plastics (PVC/ABS) |
| Weight | Very light | Light | Heavy | Light |
| Corrosion resistance | Absolute, no rust | Good if gelcoat is applied | Requires coating or plating, prone to oxidation | Poor in saltwater |
| Technical forming capability | Highly flexible, seamless monolithic molding | Good, but requires dedicated molds | Limited, requires multiple machining steps | Limited, restricted to available molds |
| Structural strength | Moderate to good with foam support | Good if reinforced | Very high, strong impact resistance | Poor, brittle under impact |
| Maintenance and replacement | Low maintenance, easy to recycle | Difficult to repair, not recyclable | Requires periodic maintenance | Ages quickly, requires frequent replacement |
Technical considerations during installation and use of HDPE buoys

Wall thickness requirements and material loading ratio in the mold
In the rotational molding process, wall thickness directly affects durability, load-bearing capacity, and outdoor service life. Therefore, it is necessary to:
- Ensure a minimum wall thickness of 6 mm to 12 mm, depending on buoy size and installation environment (river, sea, or high-wave areas requiring greater thickness)
- Accurately calculate the material loading ratio to ensure even distribution and avoid uneven walls, air voids, or thin edges
- After molding, verify wall thickness using ultrasonic measurement equipment to ensure the product meets technical standards
Methods for bolting, fastening, and connecting with steel components
HDPE cannot be directly welded to metal. To connect mooring hooks, anchor rings, or load-bearing components, it is necessary to:
- Mold embedded steel inserts or pre-installed threaded fasteners directly into the mold during production
- For externally mounted bolts, use EPDM rubber gaskets, non-corrosive metal washers, and avoid over-tightening to prevent HDPE cracking
- Place high-load components such as lifting points and mooring rings in thicker wall areas and reinforce them with foam cores or load-bearing inserts
Precautions to avoid scratches and sharp objects during operation
Although HDPE offers good impact resistance, its surface can still be scratched when in direct contact with rough concrete, sharp rocks, or rusted steel equipment. Therefore:
- Rubber padding or smooth plastic sheets should be applied at frequent contact points
- Avoid dragging buoys during relocation; instead, use soft lifting slings or auxiliary floating supports
- After each maintenance cycle, inspect and repair major scratches using plastic welding or specialized protective coatings
The future of HDPE rotomolding in the buoy and floating equipment industry

The trend of replacing traditional materials in smart cities
With increasing demands for durable, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and low-maintenance materials, HDPE rotomolding is gradually replacing buoys made from:
- Steel (prone to rust, heavy, and costly to maintain)
- FRP composites (difficult to repair and expensive)
Smart cities and modern ports are prioritizing HDPE materials for flood warning buoys, vessel positioning, and waterway channeling systems that are functional, visually consistent, and standardized.
HDPE rotomolding combined with IoT as a foundation for sensor-based and remotely monitored buoys
Thanks to its non-conductive properties, resistance to signal interference, and good thermal insulation, HDPE buoys can easily integrate modern technologies such as:
- Solar-powered LED lights
- GPS devices, tilt sensors, and water level sensors
- LoRa and NB-IoT data transmission modules connected to central control systems
This enables the development of automated buoy networks with precise positioning and real-time alerts, aligning with digital transformation and smart transportation strategies in the near future.
Conclusion
Rotationally molded HDPE is proving its superior position in the field of navigation buoy manufacturing thanks to its high durability, seamless monolithic structure, excellent corrosion resistance, and outstanding adaptability to aquatic environments. Beyond traditional buoy applications, HDPE also enables the integration of modern technologies such as sensors, GPS, and solar energy systems, bringing inland waterway transportation closer to the vision of smart, sustainable, and low-maintenance infrastructure.
FAQ
Can rotationally molded HDPE buoys withstand strong impacts?
Yes. HDPE has high flexibility and elasticity, allowing it to absorb impact forces more effectively than many rigid materials such as composite. When impacted by small vessels or floating debris, HDPE buoys typically suffer only minor surface scratches without structural cracking or breakage.
Is it possible to mold multiple colors on a single buoy body?
Yes. During the rotomolding process, manufacturers can use different color pellets for different mold sections, creating buoys with clearly segmented colors (for example, a red body and a white topmark) without the need for surface painting. This approach helps colors last longer and provides better resistance to fading.
How often should HDPE buoys be inspected?
Depending on the installation location (inland waters or marine environments), buoys should be inspected at least once per year:
– Checking positioning systems (GPS)
– Inspecting lighting systems and solar panels
– Observing surface conditions, mooring connections, and major scratches
HDPE buoys do not require frequent maintenance, but periodic inspections are still essential to ensure stable and reliable operation.
Is HDPE environmentally friendly and recyclable?
Yes. HDPE is a thermoplastic material that can be 100% recycled into other products after use, such as plastic pipes or industrial plastic chairs. The material contains no heavy metals, is non-toxic, and does not break down into microplastics in water, helping to minimize environmental impact.
Can HDPE buoys be used long-term in seawater without damage?
Absolutely. HDPE does not oxidize or corrode in saltwater, does not rust like steel, and does not delaminate like composite materials. With UV protection and a seamless monolithic structure, HDPE buoys can operate stably for 10–15 years in marine environments without replacement.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt






